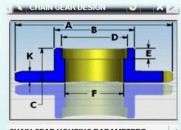
请使用QQ关联注册PLM之家,学习更多关于内容,更多精彩原创视频供你学习!
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?注册
x
The examples show how to access the following relationships:
. V* h2 V1 d H. w/ n- JNX session → list of parts part → list of solid bodies solid body → list of faces solid body → list of edges face → list of associated edges face → solid body edge → list of associated faces edge → solid body ! a( O6 e9 d' s) c$ b0 Q1 ~& X
. [2 u. |1 r Y3 Z% n/ S j5 W
Bodies, Faces and Edges - Language Specific Details
+ V R9 r3 t2 C. G" e9 p l( t4 eNX Open for C++ NX Open for .NET NX Open for Java
9 |, D7 f% I, Q; }2 b! B, }! N9 {/ E8 R% U+ S8 n0 }
NX Open for C++- x D6 S: o! I" ]) J! v
{; j5 F- J e/ k. l" p! J
& U6 Q9 M ~9 HNX session → list of parts
+ a8 {. N; ?" Q! U* H4 p) uTo access all parts in an NX session, use the Parts property to access the Part Collection. Then use the collection's iterator to access each part. Session *NXSession = Session::GetSession(); ParTCollection *partList = NXSession->Parts(); PartCollection::iterator itr; for ( itr = partList->begin(); itr != partList->end(); ++itr ) { processPart(*itr); }
) q8 ~* y& K: B6 t( y$ |7 e& ?) |: a2 u$ V. b4 C A1 A4 c y
part → list of solid bodies
) b, o) s" G# mTo access all solid bodies in a part, use the Bodies property to access the Body Collection. Then use the collection's iterator to access each body. void processPart(Part *partObject){ BodyCollection *bodyList = partObject->Bodies(); BodyCollection::iterator itr; for (itr = bodyList->begin(); itr != bodyList->end(); ++itr) { processBodyFaces(*itr); processBodyEdges(*itr); }}
1 F2 N( G& \$ H5 N" F3 W8 v9 O# N# [& y6 q0 V$ D! w
solid body → list of faces+ l! y. l+ z* N# O2 t3 W) m# B+ _8 J
To access the faces of a body use the GetFaces() method to return an array of faces. void processBodyEdges(Body *bodyObject){ std::vector <Edge *> edgeArray = bodyObject->GetEdges(); for (int inx = 0; inx < (int)edgeArray.size(); ++inx) { processEdge(edgeArray[inx]); }} / X1 \8 k" a- g5 T0 T! ?' e
9 ^. Y7 n9 O$ I
solid body → list of edges
7 @7 f U& V# ]To access the edges in a body use the GetEdges() method to return an array of edges. void processBodyEdges(Body *bodyObject){ std::vector <Edge *> edgeArray = bodyObject->GetEdges(); for (int inx = 0; inx < (int)edgeArray.size(); ++inx) { processEdge(edgeArray[inx]); }}
5 q6 `. ^* n2 P* \( V3 P9 r- h
0 Q, c3 r/ O" J0 h$ W A: A# Xface → list of associated edges
3 T/ v) N: C; h4 [8 X; v" ]face → solid body
8 |' m( t, {. F5 k& P6 {6 N& X; f: ~To access the edges for a face use the GetEdges() method to return an array of edges. To access the face's body use the GetBody() method. void processFace(Face *faceObject){ std::vector<Edge *> edgeArray = faceObject->GetEdges(); for (int inx = 0; inx < (int)edgeArray.size(); ++inx) { processEdge(edgeArray[inx]); } Body *bodyOfFace = faceObject->GetBody();} , N3 ~# t6 \- L; S5 P2 H2 Q5 w
" k2 N0 P2 b: f: Y
edge → list of associated faces
3 O1 U+ t# e2 V; ~4 D- bedge → solid body) u5 i; J5 ]2 f8 I+ C J
To access the faces associated with and edge use the GetFaces() method to return an array of faces. To access the edge's body use the GetBody() method. void processEdge(Edge *edgeObject){ std::vector<Face *> faceArray = edgeObject->GetFaces(); for (int inx = 0; inx < (int)faceArray.size(); ++inx) { processEdgeFace(faceArray[inx]); } Body *bodyOfEdge = edgeObject->GetBody();}
8 i; y1 L( z P. |- z |